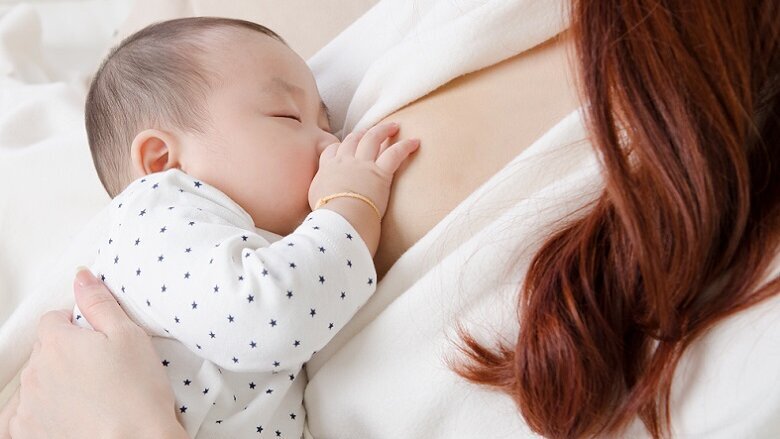
BRISBANE, Australia: There is much debate of the pros and cons of breast- and bottle-feeding. A research team from the Queensland University of Technology (QUT), in collaboration with the University of Queensland, both in Australia, has found that breastfeeding, at least in terms of oral health of the baby, is beneficial.
According to lead author Dr Emma Sweeney, from the Institute of Health and Biomedical Innovation at QUT, the team’s earlier studies had found significant differences in the prevalence of key bacteria in the mouths of breastfed and formula-fed babies and that breastmilk and saliva interactions boost innate immunity by acting in synergy to regulate the oral microbiome of newborn babies.
For the recent study, a variety of microorganisms were exposed to breastmilk and saliva mixtures. The results showed that inhibited growth of the microorganisms took place immediately and for up to one day regardless of whether the microorganisms were considered pathogenic or commensal in an infant’s mouth.
“Our findings suggest that breastmilk is more than a simple source of nutrition for babies because it plays an important role in shaping a healthy oral microbiome,” said Sweeney. “Our previous research found that the interaction of neonatal saliva and breast milk releases antibacterial compounds, including hydrogen peroxide. The release of this chemical compound also activates the lactoperoxidase system, which produces additional compounds that also have antibacterial activity, and these compounds are capable of regulating the growth of microorganisms,” she added.
According to the research team, the composition of a baby’s mouth microbiota has an important role in its health and well-being and also has an impact on infections and diseases in babies’ early lives.
The study, titled “The effect of breastmilk and saliva combinations on the in vitro growth of oral pathogenic and commensal microorganisms”, was published online in Scientific Reports on 11 October 2018.
Tags:
PHILADELPHIA, US: Periodontitis is one of the world’s most prevalent health conditions, affecting between 20% and 50% of the global population—roughly ...
NEW YORK, US: Oral diseases and depression are both projected to rise in prevalence over the coming decades, and recent findings suggest the two may be ...
BELFAST, UK: It remains controversial whether poor oral health is independently linked to the development of gastro-intestinal cancers, because of potential...
BILBAO, Spain: While the systemic health implications of neuropsychiatric disorders are well recognised, their connection to poor oral health—in ...
COPENHAGEN, Denmark: A number of recent studies have shown that dental calculus from archaeological samples could be a rich source for better understanding ...
OKAYAMA, Japan: Since periodontitis has been linked to systemic health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer and Alzheimer’s disease, ...
SOLNA, Sweden: The oral cavity represents a complex microenvironment where a diverse microbial community flourishes. A recent review study, carried out by ...
COPENHAGEN, Denmark: Though its popularity and constituent ingredients have changed over time, chewing gum has been used by humans for thousands of years. A...
ORADEA, Romania: Ongoing research continues to illuminate the plethora of ways in which oral and systemic health influence each other. While odontogenic ...
DALLAS, US: An increased burden of cerebrovascular disease could be connected to a genetic predisposition for poor oral health, according to a new study ...
Live webinar
Tue. 10 February 2026
7:00 pm EST (New York)
Prof. Dr. Wael Att, Dr. Robert A. Levine DDS, FCPP, FISPPS, AOD, Dr. Larissa Bemquerer ITI Scholar at Harvard
Live webinar
Wed. 11 February 2026
11:00 am EST (New York)
Dr. med. dent. Sven Mühlemann
Live webinar
Wed. 11 February 2026
12:00 pm EST (New York)
Prof. Dr. Samir Abou Ayash
Live webinar
Fri. 13 February 2026
12:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Mon. 16 February 2026
12:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Tue. 17 February 2026
12:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Wed. 18 February 2026
9:00 am EST (New York)
Dr. Anna Lella, Ms. Francesca Nava



 Austria / Österreich
Austria / Österreich
 Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
 Bulgaria / България
Bulgaria / България
 Croatia / Hrvatska
Croatia / Hrvatska
 Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
 France / France
France / France
 Germany / Deutschland
Germany / Deutschland
 Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
 Hungary / Hungary
Hungary / Hungary
 Italy / Italia
Italy / Italia
 Netherlands / Nederland
Netherlands / Nederland
 Nordic / Nordic
Nordic / Nordic
 Poland / Polska
Poland / Polska
 Portugal / Portugal
Portugal / Portugal
 Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
 Slovenia / Slovenija
Slovenia / Slovenija
 Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
 Spain / España
Spain / España
 Switzerland / Schweiz
Switzerland / Schweiz
 Turkey / Türkiye
Turkey / Türkiye
 UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
 Brazil / Brasil
Brazil / Brasil
 Canada / Canada
Canada / Canada
 Latin America / Latinoamérica
Latin America / Latinoamérica
 USA / USA
USA / USA
 China / 中国
China / 中国
 India / भारत गणराज्य
India / भारत गणराज्य
 Pakistan / Pākistān
Pakistan / Pākistān
 Vietnam / Việt Nam
Vietnam / Việt Nam
 ASEAN / ASEAN
ASEAN / ASEAN
 Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
 Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
 Middle East / Middle East
Middle East / Middle East







































To post a reply please login or register