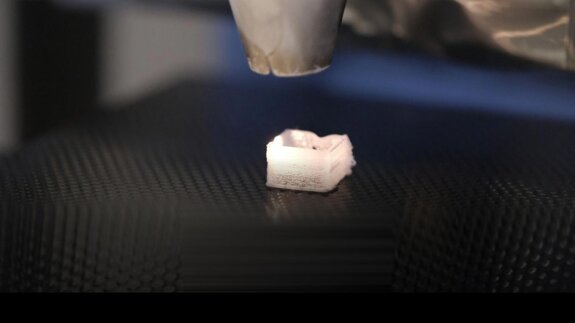
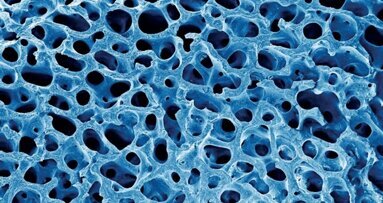
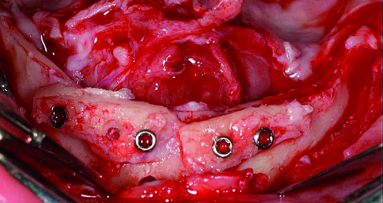
Objective: Compared with hydroxyapatite, alpha-tricalcium phosphate (α-TCP) is more biodegradable and shows better integration during physiological bone remodeling. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effects of porous α-TCP as a tissue-engineered scaffold for maxillary sinus augmentation in a canine model.
Materials and methods
Porous α-TCP was prepared by pulverizing an α-TCP block with an 80% continuous pore structure. Bilateral sinus floor augmentation surgeries were performed on beagle dogs that were randomly divided into two groups based on the type of repair: The experimental group received a porous α-TCP and titanium (Ti) implant, and the control group received a Ti implant. Periimplant bone volume (BV) and bone mineral content (BMC) were measured and analyzed using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and Villanueva–Goldner staining for histological examination. The intergroup differences were evaluated using the Student’s t-test.
Results
Micro-CT images at 12 weeks after surgery showed higher BV and BMC in the experimental group than in the control group (p < 0.05). Histological examination showed high levels of α-TCP even at four weeks, but the scaffolds were completely absorbed and new bone integrated into the Ti implants at 12 and 24 weeks. However, no bone formation was observed in the control group throughout the study.
Conclusions
Porous α-TCP increased BV and promoted bone mineralization and earlier bone formation in the augmented maxillary sinus. Therefore, this tissue-engineered scaffold might be a better alternative to autologous bone for maxillary sinus augmentation.
Editorial note: The full article was published in the 1/2017 issue of the Journal of Oral Science and Rehabilitation. It can be accessed free of charge at www.dtscience.com.
The use of 3D imaging has become the standard of care for diagnosis and treatment planning for many medical and dental procedures. Such imaging was first ...
Ectopic canines are a complex condition to treat with aligners only, since it is not easy to create a reliable and stable anchorage unit for forced ...
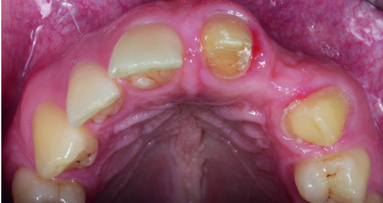
Objective: Bone resorption of maxillary ridges is an unavoidable process that occurs after tooth extraction. Many treatment alternatives have been proposed ...
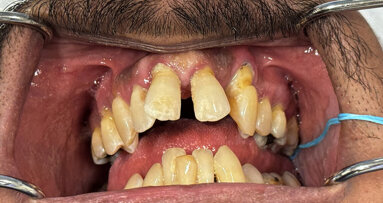
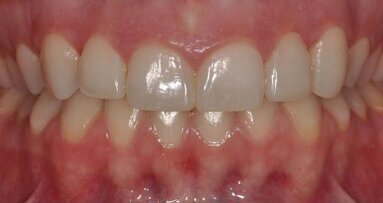
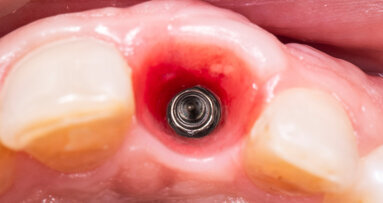
In the case presented, the treatment plan was to place a single implant in the aesthetically demanding anterior maxillary region in the place of the left ...
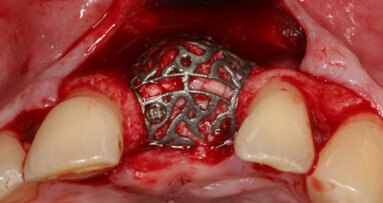
The most important innovation in recent years in the field of guided bone regeneration (GBR) is customised CAD/CAM titanium meshes, which allow for ...
Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technologies may improve application of titanium scaffolds, onlay techniques and guided bone ...
Success in aesthetic dentistry relies largely on the ability to understand the patient’s chief complaint clearly and expectations in seeking dental ...
Prof. Kamal Mustafa from the Department of Clinical Dentistry at the University of Bergen in Norway is sponsoring and leading, together with Dr Cecilie ...
LUCERNE, Switzerland: Earlier this year, 43 leading experts from three organisations participated in a unique consensus meeting. The aim of the meeting was ...
An adequate bone volume at the future implant site is a prerequisite for ideal implant placement and implant success. A residual bone with a vertical ...
Live webinar
Tue. 3 March 2026
11:00 am EST (New York)
Dr. Omar Lugo Cirujano Maxilofacial
Live webinar
Tue. 3 March 2026
8:00 pm EST (New York)
Dr. Vasiliki Maseli DDS, MS, EdM
Live webinar
Wed. 4 March 2026
12:00 pm EST (New York)
Munther Sulieman LDS RCS (Eng) BDS (Lond) MSc PhD
Live webinar
Wed. 4 March 2026
1:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Fri. 6 March 2026
3:00 am EST (New York)
Live webinar
Tue. 10 March 2026
4:00 am EST (New York)
Assoc. Prof. Aaron Davis, Prof. Sarah Baker
Live webinar
Tue. 10 March 2026
8:00 pm EST (New York)
Dr. Vasiliki Maseli DDS, MS, EdM



 Austria / Österreich
Austria / Österreich
 Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
 Bulgaria / България
Bulgaria / България
 Croatia / Hrvatska
Croatia / Hrvatska
 Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
 France / France
France / France
 Germany / Deutschland
Germany / Deutschland
 Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
 Hungary / Hungary
Hungary / Hungary
 Italy / Italia
Italy / Italia
 Netherlands / Nederland
Netherlands / Nederland
 Nordic / Nordic
Nordic / Nordic
 Poland / Polska
Poland / Polska
 Portugal / Portugal
Portugal / Portugal
 Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
 Slovenia / Slovenija
Slovenia / Slovenija
 Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
 Spain / España
Spain / España
 Switzerland / Schweiz
Switzerland / Schweiz
 Turkey / Türkiye
Turkey / Türkiye
 UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
 Brazil / Brasil
Brazil / Brasil
 Canada / Canada
Canada / Canada
 Latin America / Latinoamérica
Latin America / Latinoamérica
 USA / USA
USA / USA
 China / 中国
China / 中国
 India / भारत गणराज्य
India / भारत गणराज्य
 Pakistan / Pākistān
Pakistan / Pākistān
 Vietnam / Việt Nam
Vietnam / Việt Nam
 ASEAN / ASEAN
ASEAN / ASEAN
 Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
 Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
 Middle East / Middle East
Middle East / Middle East


































To post a reply please login or register