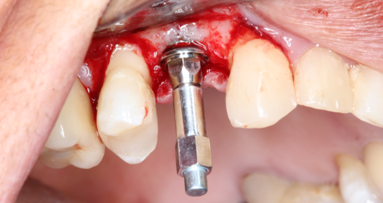
In recent years, periimplantitis has been extensively studied as bone loss has been observed around dental implants. As a result of multiple factors, different materials might enhance different patterns of bacterial plaque accumulation. The purpose of this research was to assess bacterial adhesion to different abutments and define the efficacy of different detersion protocols in reducing bacterial adhesion.
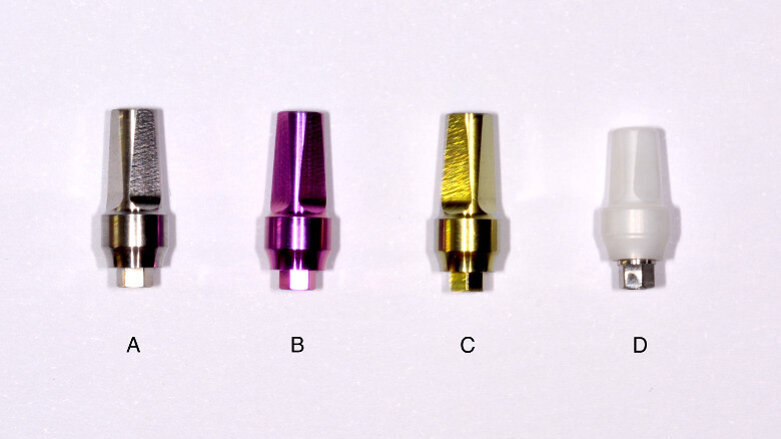
Methods: Four kinds of prefabricated abutments were analyzed: machined pure titanium abutments without anodization, machined gold hue and pink hue anodized pure titanium abutments and zirconia abutments with titanium connectors. All of the (sterile) abutments were immersed in separate bacterial suspensions (Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Streptococcus pyogenes and Escherichia coli) and contaminated with 3 × 108 colony-forming units per mL of each bacterial species suspension. Then, the following detersion protocols were compared: no treatment representing the internal control, 10 min rinsing with water, 10 min incubation in 0.05% chlorhexidine. The microbial abatement was determined by swab collection of abutment-attached microbes and swab streaking on specific culture plates in a semiquantitative manner. Microbial growth was determined at 24 and 48 hours after inoculation.
Results: Contaminated abutments that had not undergone any cleaning treatment displayed a microbial growth up to the third quadrant of the culture plate. Chlorhexidine rinsing completely removed bacterial contamination. No statistically significant differences were found in terms of bacterial adhesion and bacterial growth among the different types of abutments.
Conclusion: All of the analyzed abutments displayed similar characteristics with regard to bacterial adhesion. A low concentration of chlorhexidine had a significant disinfectant activity, regardless of the type of abutment.
Editorial note: The full article was published in the 1/2018 issue of the Journal of Oral Science and Rehabilitation.
Tags:
The long-term clinical success of dental implants is dependent upon osseointegration, which is defined as a direct functional and structural connection ...
Dental technicians have so many different restorative materials and design and finishing concepts available to them that it can seem difficult to select the...
KHON KAEN, Thailand: Orofacial clefts (OFCs) occur at a slightly higher rate in Asia than elsewhere—1.6 cases per 1,000 live births compared with one in...
HONG KONG, China: Moisture is one of the greatest challenges for dental fillings, as it reduces adhesive performance. To overcome this obstacle, researchers...
SENDAI, Japan: Researchers at Tohoku University in Japan have found that maternal mental health may play a significant role in instilling early ...
ZAGREB, Croatia: As 3D-printed aligners gain traction, many patients and clinicians continue to apply cleaning routines that were originally developed for ...
LONDON, England: One of the key promises of artificial intelligence-based (AI-based) tools in dentistry is the expediting of time-consuming tasks. The ...
The introduction of the nickel-titanium (NiTi) alloy in endodontics was a significant improvement, allowing good results in terms of cleaning and shaping of...
The aim of this case presentation is to show a step-by-step workflow with Atlantis patient-specific abutments. The case is of a 36-year-old patient with a ...
WASHINGTON, US: Covering everything, including composite fillings and disposable suction tips, plastics are woven into all aspects of modern dental care. ...
Live webinar
Tue. 17 March 2026
8:00 am EST (New York)
Live webinar
Tue. 17 March 2026
1:00 pm EST (New York)
Prof. Dr. Nadine Schlüter
Live webinar
Tue. 17 March 2026
1:00 pm EST (New York)
Dr. Giuseppe Luongo MD, DDS, Dr. Fabrizia Luongo DMD, MS
Live webinar
Wed. 18 March 2026
7:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Thu. 19 March 2026
1:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Fri. 20 March 2026
5:00 am EST (New York)
Mr. Andrew Terry Cert.DT. GradDipDH. Med, Cat Edney
Live webinar
Mon. 23 March 2026
9:30 am EST (New York)
Prof. Gianluca Gambarini MD, DDS



 Austria / Österreich
Austria / Österreich
 Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
 Bulgaria / България
Bulgaria / България
 Croatia / Hrvatska
Croatia / Hrvatska
 Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
 France / France
France / France
 Germany / Deutschland
Germany / Deutschland
 Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
 Hungary / Hungary
Hungary / Hungary
 Italy / Italia
Italy / Italia
 Netherlands / Nederland
Netherlands / Nederland
 Nordic / Nordic
Nordic / Nordic
 Poland / Polska
Poland / Polska
 Portugal / Portugal
Portugal / Portugal
 Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
 Slovenia / Slovenija
Slovenia / Slovenija
 Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
 Spain / España
Spain / España
 Switzerland / Schweiz
Switzerland / Schweiz
 Turkey / Türkiye
Turkey / Türkiye
 UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
 Brazil / Brasil
Brazil / Brasil
 Canada / Canada
Canada / Canada
 Latin America / Latinoamérica
Latin America / Latinoamérica
 USA / USA
USA / USA
 China / 中国
China / 中国
 India / भारत गणराज्य
India / भारत गणराज्य
 Pakistan / Pākistān
Pakistan / Pākistān
 Vietnam / Việt Nam
Vietnam / Việt Nam
 ASEAN / ASEAN
ASEAN / ASEAN
 Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
 Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
 Middle East / Middle East
Middle East / Middle East







































To post a reply please login or register