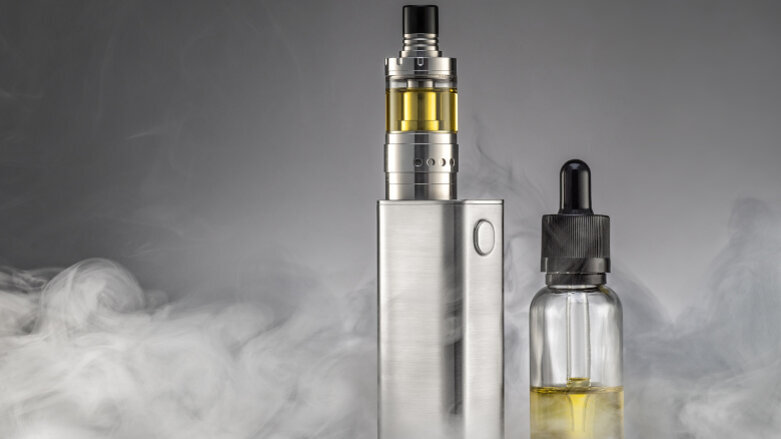
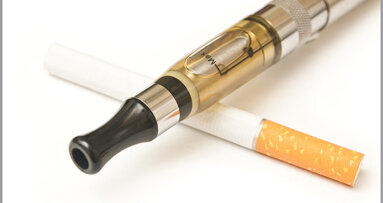
BOSTON, U.S.: Cigarette smoke contains microbes and microbial toxins, such as endotoxin and glucan, that may have adverse respiratory effects. However, the potential for contamination of e-cigarette products sold in the U.S. has not yet been investigated. A new study aimed to fill that gap and reported that e-cigarette products sold in the U.S. are contaminated with bacterial and fungal toxins and therefore may pose serious respiratory health risks.
Researchers from the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (Harvard Chan School) examined 75 popular e-cigarette products. They classified the products into four flavor categories—tobacco, menthol, fruit and other—and then screened them for the presence of endotoxin and glucan.
The findings showed that 17 products contained detectable concentrations of endotoxin, whereas 61 products contained detectable concentrations of glucan. Further analysis revealed that cartridge samples had 3.2 times higher concentrations of glucan than the e-liquid samples. Glucan concentrations were also significantly higher in tobacco- and menthol-flavored products, compared with fruit-flavored products. However, fruit-flavored products were higher in endotoxin concentrations, which indicates that raw materials used in the production of flavors might be a source of microbial contamination, according to the research team.
“Airborne Gram-negative bacterial endotoxin and fungal-derived glucans have been shown to cause acute and chronic respiratory effects in occupational and environmental settings,” said senior author Dr. David Christiani, Elkan Blout Professor of Environmental Genetics at the school. “Finding these toxins in e-cigarette products adds to the growing concerns about the potential for adverse respiratory effects in users.” Previous research from the Harvard Chan School has shown that chemicals linked with severe respiratory disease are found in common e-cigarette flavors.
The researchers noted that the contamination may occur at any point during the production of the ingredients or of the finished e-cigarette product. According to them, the cotton wicks used in e-cigarette cartridges may be one source of contamination, as both endotoxin and glucan are known contaminants of cotton fibers. “In addition to inhaling harmful chemicals, e-cig users could also be exposed to biological contaminants like endotoxin and glucan,” said lead author Dr. Mi-Sun Lee, a research fellow at the school. “These new findings should be considered when developing regulatory policies for e-cigarettes,” Lee concluded.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, e-cigarette use among American high school students increased by 78 percent between 2017 and 2018, and by 48 percent among middle schoolers.
The study, titled “Endotoxin and (1→3)-β-D-glucan contamination in electronic cigarette products sold in the United States,” was published online in the April 2019 issue of Environmental Health Perspectives.
Tags:
ATLANTA, U.S.: The issue of e-cigarettes and their health risks has always been contentious. In a recent study, researchers from Georgia State University ...
CLEVELAND, U.S: The controversy over the safety of electronic cigarettes persists, and some people regard vaping as a public health epidemic. Experts have ...
BOSTON, U.S.: Electronic cigarettes are becoming increasingly popular. Although they are viewed by some as a safer alternative to smoking, their effects are...
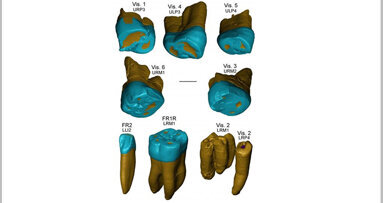
TOULOUSE, France: In a recent study, French, Italian and Spanish researchers have investigated some of the oldest fossil dental remains from Middle ...
NEW YORK, U.S.: Throughout history, human exposure to various metals and its effects have been investigated numerous times. In a new study, scientists from ...
GLASGOW, UK: According to research presented at the recent annual National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference in Glasgow, 29 per cent of ...
PHILADELPHIA, U.S.: The dangers of smoking are well known, and in a new study, researchers have pinpointed it as being a major factor in developing head and...
CLEVELAND, U.S.: Obesity and periodontal disease remain the most common noncommunicable diseases in the U.S. A recent study has explored the effect of ...
OKAYAMA, Japan: In a recent study, researchers from Okayama University investigated whether involuntary masseter muscle activity showed any specific pattern...
ANN ARBOR, Mich., US: As the number of dental implants placed globally continues to rise, so too does the clinical significance of understanding ...
Live webinar
Wed. 4 March 2026
8:30 pm EST (New York)
Lancette VanGuilder BS, RDH, PHEDH, CEAS, FADHA
Live webinar
Fri. 6 March 2026
3:00 am EST (New York)
Live webinar
Mon. 9 March 2026
12:30 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Mon. 9 March 2026
3:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Tue. 10 March 2026
4:00 am EST (New York)
Assoc. Prof. Aaron Davis, Prof. Sarah Baker
Live webinar
Tue. 10 March 2026
8:00 pm EST (New York)
Dr. Vasiliki Maseli DDS, MS, EdM
Live webinar
Wed. 11 March 2026
12:00 pm EST (New York)
MDT Andreas Chatzimpatzakis



 Austria / Österreich
Austria / Österreich
 Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
 Bulgaria / България
Bulgaria / България
 Croatia / Hrvatska
Croatia / Hrvatska
 Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
 France / France
France / France
 Germany / Deutschland
Germany / Deutschland
 Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
 Hungary / Hungary
Hungary / Hungary
 Italy / Italia
Italy / Italia
 Netherlands / Nederland
Netherlands / Nederland
 Nordic / Nordic
Nordic / Nordic
 Poland / Polska
Poland / Polska
 Portugal / Portugal
Portugal / Portugal
 Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
 Slovenia / Slovenija
Slovenia / Slovenija
 Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
 Spain / España
Spain / España
 Switzerland / Schweiz
Switzerland / Schweiz
 Turkey / Türkiye
Turkey / Türkiye
 UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
 Brazil / Brasil
Brazil / Brasil
 Canada / Canada
Canada / Canada
 Latin America / Latinoamérica
Latin America / Latinoamérica
 USA / USA
USA / USA
 China / 中国
China / 中国
 India / भारत गणराज्य
India / भारत गणराज्य
 Pakistan / Pākistān
Pakistan / Pākistān
 Vietnam / Việt Nam
Vietnam / Việt Nam
 ASEAN / ASEAN
ASEAN / ASEAN
 Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
 Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
 Middle East / Middle East
Middle East / Middle East


































To post a reply please login or register