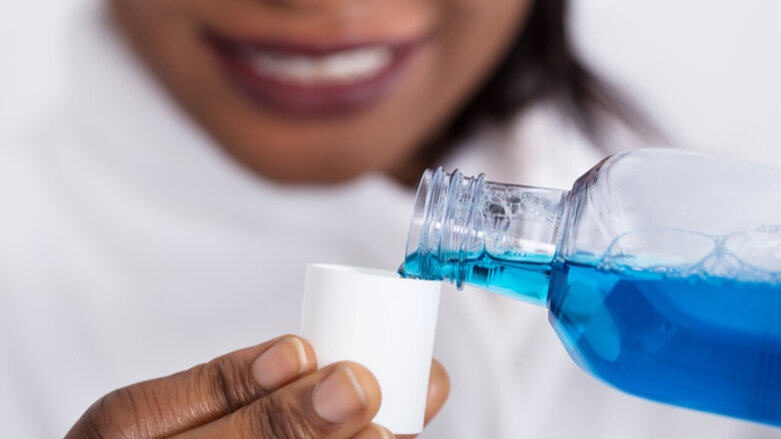
LEIOA, Spain: The human oral cavity is populated by a variety of bacteria. Surgical procedures in the mouth thus pose the risk of bacteria passing into the bloodstream, causing bacteraemia. This is generally transient; however, it is not yet clear how bacteria in the blood are associated with the origin and evolution of infectious processes. Previous studies have shown that chlorhexidine mouthwashes have an antimicrobial effect on saliva and bacterial plague. However, a research team from the University of the Basque Country has now found that chlorhexidine mouthwashes have only an insignificant prophylactic effect regarding oral procedures.
To assess the effectiveness of chlorhexidine in preventing bacteraemia after a tooth extraction, the research group conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled clinical trials. The study included eight clinical trials with a total of 523 patients. Of these, 267 were treated with chlorhexidine, among whom 145 cases of bacteraemia were recorded. The control group consisted of 256 patients, in which 156 cases of bacteraemia were found. The results therefore indicate that 12 per cent of bacteraemia cases could be prevented with chlorhexidine-based prophylaxis.
The results point to the relative and not particularly significant effectiveness of chlorhexidine with respect to preventing bacteria in the mouth from passing into the bloodstream during dental extractions. “Yet, given its low cost and the absence of adverse reactions and complications, we would recommend a mouthwash with chlorhexidine before a procedure of this type is carried out,” concluded the research group.
The study, titled “Does chlorhexidine reduce bacteremia following tooth extraction? A systematic review and meta-analysis”, was published on 23 April 2018 in PLOS ONE.
Tags:
AMMAN, Jordan: As artificial intelligence continues to expand its role in healthcare, large language models such as ChatGPT are increasingly being used to ...
OSLO, Norway: Alleviating stress for fearful dental patients, especially vulnerable ones such as children, is of paramount concern for dentists. Now, a ...
SEOUL, South Korea: Even though intra-oral scanners have been around for more than three decades and their use in dental practice is increasing, few ...
NEW YORK, US: Oral diseases and depression are both projected to rise in prevalence over the coming decades, and recent findings suggest the two may be ...
BOSTON, U.S.: It has been well established that early detection of oral cancer is key for successful treatment and an optimal outcome. In a concerning piece...
TAIPEI, Taiwan: The debate on climate change and its effects on the earth are a hot topic. One discussion, in particular, is around air pollution, which is ...
SYDNEY, Australia: The links between oral health and overall health are numerous, with their importance continually filtering into broader society. In a new...
SEATTLE, U.S.: Owing to its easy application, its affordable price and the low risk of swallowing the product, fluoride varnish (FV) has become a popular ...
ORADEA, Romania: Ongoing research continues to illuminate the plethora of ways in which oral and systemic health influence each other. While odontogenic ...
ADELAIDE, Australia: Research carried out at the University of Adelaide has examined the relationship between previous orthodontic treatment and improved ...
Live webinar
Tue. 17 March 2026
8:00 am EST (New York)
Live webinar
Tue. 17 March 2026
1:00 pm EST (New York)
Prof. Dr. Nadine Schlüter
Live webinar
Tue. 17 March 2026
1:00 pm EST (New York)
Dr. Giuseppe Luongo MD, DDS, Dr. Fabrizia Luongo DMD, MS
Live webinar
Wed. 18 March 2026
7:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Thu. 19 March 2026
1:00 pm EST (New York)
Live webinar
Fri. 20 March 2026
5:00 am EST (New York)
Mr. Andrew Terry Cert.DT. GradDipDH. Med, Cat Edney
Live webinar
Mon. 23 March 2026
9:30 am EST (New York)
Prof. Gianluca Gambarini MD, DDS



 Austria / Österreich
Austria / Österreich
 Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
Bosnia and Herzegovina / Босна и Херцеговина
 Bulgaria / България
Bulgaria / България
 Croatia / Hrvatska
Croatia / Hrvatska
 Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
Czech Republic & Slovakia / Česká republika & Slovensko
 France / France
France / France
 Germany / Deutschland
Germany / Deutschland
 Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
Greece / ΕΛΛΑΔΑ
 Hungary / Hungary
Hungary / Hungary
 Italy / Italia
Italy / Italia
 Netherlands / Nederland
Netherlands / Nederland
 Nordic / Nordic
Nordic / Nordic
 Poland / Polska
Poland / Polska
 Portugal / Portugal
Portugal / Portugal
 Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
Romania & Moldova / România & Moldova
 Slovenia / Slovenija
Slovenia / Slovenija
 Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
Serbia & Montenegro / Србија и Црна Гора
 Spain / España
Spain / España
 Switzerland / Schweiz
Switzerland / Schweiz
 Turkey / Türkiye
Turkey / Türkiye
 UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
UK & Ireland / UK & Ireland
 Brazil / Brasil
Brazil / Brasil
 Canada / Canada
Canada / Canada
 Latin America / Latinoamérica
Latin America / Latinoamérica
 USA / USA
USA / USA
 China / 中国
China / 中国
 India / भारत गणराज्य
India / भारत गणराज्य
 Pakistan / Pākistān
Pakistan / Pākistān
 Vietnam / Việt Nam
Vietnam / Việt Nam
 ASEAN / ASEAN
ASEAN / ASEAN
 Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
Israel / מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל
 Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
Algeria, Morocco & Tunisia / الجزائر والمغرب وتونس
 Middle East / Middle East
Middle East / Middle East




































To post a reply please login or register